When it comes to permanent magnets, one of the most critical properties that determines their performance is the direction of magnetization. Understanding this concept is essential for engineers, product designers, and manufacturers who rely on magnets for industrial, commercial, and consumer applications.
What is Direction of Magnetization?
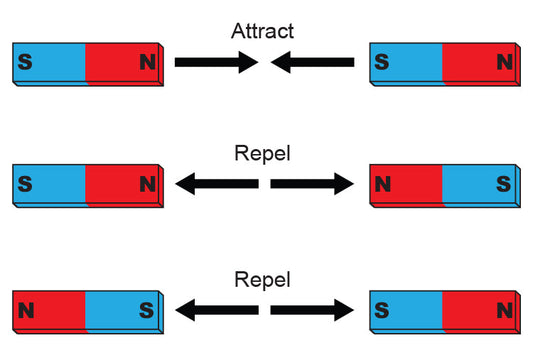
The direction of magnetization refers to the orientation of the magnetic field inside a magnet. It defines how the magnetic poles (north and south) are aligned and where the magnetic force will be strongest. This alignment is determined during the manufacturing process and cannot be changed later without demagnetizing and remagnetizing the material.
Why is Direction of Magnetization Important?
Choosing the correct magnetization direction is crucial because it directly impacts how a magnet interacts with its surroundings. Whether a magnet is used in motors, sensors, speakers, or holding applications, its effectiveness depends on aligning the magnet’s poles with the intended function.
- Optimal Performance: Correct alignment ensures maximum magnetic strength in the desired direction.
- Design Flexibility: Different applications require different orientations (axial, radial, diametric, multipole).
- Efficiency: Reduces energy loss in devices like motors and generators.
Common Types of Magnetization Directions
1.Axial Magnetization
- Poles are on the flat circular faces of a cylinder or disc magnet.
- Commonly used in sensors, magnetic couplings, and holding applications.
2.Radial Magnetization
- Poles are arranged around the circumference of the magnet.
- Ideal for ring magnets in motors and generators, providing a strong rotational field.
3.Diametric Magnetization
- Poles are on the curved sides of the magnet.
- Suitable for magnetic stirrers, rotating couplings, and special assemblies.
4.Multipole Magnetization
- Multiple north and south poles on the same surface.
- Often used in magnetic encoders, printers, and specialized sensors.
Applications Based on Magnetization Direction
- Motors & Generators: Radial and multipole magnetization enable efficient energy conversion.
- Medical Devices: Precision instruments often use axial magnetized magnets.
- Consumer Electronics: Speakers and headphones rely on carefully aligned magnetization for sound clarity.
- Industrial Holding: Axial magnets provide strong pull forces for lifting and securing objects.
Choosing the Right Magnetization for Your Application
Selecting the proper magnetization direction depends on:
- Shape of the magnet (disc, ring, block, arc).
- Intended application (rotation, holding, sensing).
- Required magnetic field strength and distribution.
Working with a trusted magnet supplier ensures that your magnets are manufactured with the correct magnetization for optimal results.
Final Thoughts
The direction of magnetization is not just a technical detail — it’s the foundation of how a magnet will perform in real-world applications. By understanding axial, radial, diametric, and multipole magnetization, designers and engineers can create efficient, powerful, and reliable solutions across industries.
Looking for customized magnets with the right magnetization direction? At Magnetyz, we provide high-performance permanent magnets tailored to your exact needs.